Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Simple dose computation#
author: OpenTPS team
In this example we are going to create a generic CT and use the MCsquare dose calculator to compute the dose image
running time: ~ 7 minute
Setting up the environment in google collab#
import sys
if "google.colab" in sys.modules:
from IPython import get_ipython
get_ipython().system('git clone https://gitlab.com/openmcsquare/opentps.git')
get_ipython().system('pip install ./opentps')
import opentps
imports
import numpy as np
import os
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import math
import the needed opentps.core packages
from opentps.core.data.images import CTImage
from opentps.core.data.images import ROIMask
from opentps.core.data.plan import ProtonPlanDesign
from opentps.core.data import DVH
from opentps.core.data import Patient
from opentps.core.io import mcsquareIO
from opentps.core.io.scannerReader import readScanner
from opentps.core.processing.doseCalculation.doseCalculationConfig import DoseCalculationConfig
from opentps.core.processing.doseCalculation.protons.mcsquareDoseCalculator import MCsquareDoseCalculator
from opentps.core.processing.imageProcessing.resampler3D import resampleImage3DOnImage3D,resampleImage3D
Generic CT creation#
we will first create a generic CT of a box fill with water and air
ctCalibration = readScanner(DoseCalculationConfig().scannerFolder)
bdl = mcsquareIO.readBDL(DoseCalculationConfig().bdlFile)
patient = Patient()
patient.name = 'Patient'
ctSize = 150
ct = CTImage()
ct.name = 'CT'
ct.patient = patient
huAir = -1024.
huWater = ctCalibration.convertRSP2HU(1.)
data = huAir * np.ones((ctSize, ctSize, ctSize))
data[:, 50:, :] = huWater
ct.imageArray = data
Region of interest#
we will now create a region of interest wich is a small 3D box of size 20*20*20
roi = ROIMask()
roi.patient = patient
roi.name = 'TV'
roi.color = (255, 0, 0) # red
data = np.zeros((ctSize, ctSize, ctSize)).astype(bool)
data[65:85, 65:85, 65:85] = True
roi.imageArray = data
Configuration of MCsquare#
to configure Mcsquare we need to calibrate it with the CT calibration obtained above
mc2 = MCsquareDoseCalculator()
mc2.beamModel = bdl
mc2.ctCalibration = ctCalibration
mc2.nbPrimaries = 1e7
Plan Creation#
we will now create a plan and create one beam
# Design plan
beamNames = ["Beam1","Beam2","Beam3"]
gantryAngles = [0.,90.,270.]
couchAngles = [0.,0.,0.]
# Generate new plan
planDesign = ProtonPlanDesign()
planDesign.ct = ct
planDesign.targetMask = roi
planDesign.gantryAngles = gantryAngles
planDesign.beamNames = beamNames
planDesign.couchAngles = couchAngles
planDesign.calibration = ctCalibration
planDesign.spotSpacing = 5.0
planDesign.layerSpacing = 5.0
planDesign.targetMargin = 5.0
plan = planDesign.buildPlan() # Spot placement
plan.PlanName = "NewPlan"
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.12.12/x64/lib/python3.12/site-packages/opentps/core/processing/planOptimization/planInitializer.py:102: UserWarning: Small proton ranges are used, accuracy of energy computation cannot be guaranteed.
warnings.warn('Small proton ranges are used, accuracy of energy computation cannot be guaranteed.')
Center of mass#
Here we look at the part of the 3D CT image where “stuff is happening” by getting the CoM. We use the function resampleImage3DOnImage3D to the same array size for both images.
roi = resampleImage3DOnImage3D(roi, ct)
COM_coord = roi.centerOfMass
COM_index = roi.getVoxelIndexFromPosition(COM_coord)
Z_coord = COM_index[2]
img_ct = ct.imageArray[:, :, Z_coord].transpose(1, 0)
contourTargetMask = roi.getBinaryContourMask()
img_mask = contourTargetMask.imageArray[:, :, Z_coord].transpose(1, 0)
#Output path
output_path = 'Output'
if not os.path.exists(output_path):
os.makedirs(output_path)
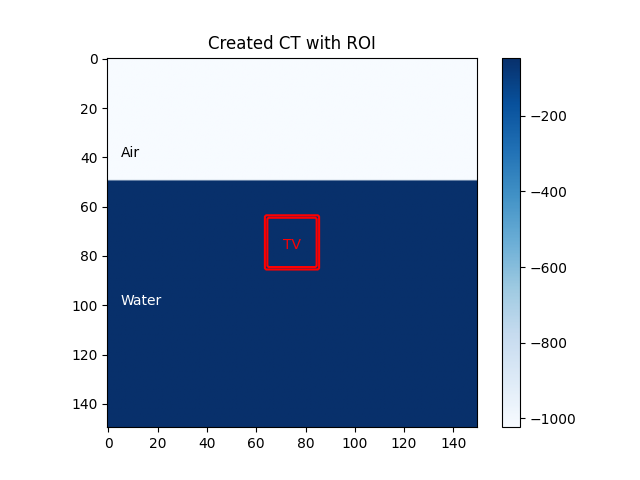
image = plt.imshow(img_ct,cmap='Blues')
plt.colorbar(image)
plt.contour(img_mask,colors="red")
plt.title("Created CT with ROI")
plt.text(5,40,"Air",color= 'black')
plt.text(5,100,"Water",color = 'white')
plt.text(71,77,"TV",color ='red')
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output_path, 'SimpleCT.png'),format = 'png')
plt.show()
Dose Computation#
We now use the MCsquare dose calculator to compute the dose of the created plan
doseImage = mc2.computeDose(ct, plan)
img_dose = resampleImage3DOnImage3D(doseImage, ct)
img_dose = img_dose.imageArray[:, :, Z_coord].transpose(1, 0)
scoringSpacing = [2, 2, 2]
scoringGridSize = [int(math.floor(i / j * k)) for i, j, k in zip([150,150,150], scoringSpacing, [1,1,1])]
roiResampled = resampleImage3D(roi, origin=ct.origin, gridSize=scoringGridSize, spacing=scoringSpacing)
target_DVH = DVH(roiResampled, doseImage)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
ax[0].imshow(img_ct, cmap='gray')
ax[0].imshow(img_mask, alpha=.2, cmap='binary') # PTV
dose = ax[0].imshow(img_dose, cmap='jet', alpha=.2)
cbar = plt.colorbar(dose, ax=ax[0])
cbar.set_label('Dose(Gy)')
ax[1].plot(target_DVH.histogram[0], target_DVH.histogram[1], label=target_DVH.name)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Dose (Gy)")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Volume (%)")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(output_path, 'SimpleDose.png'), format = 'png')
plt.show()

print('D95 = ' + str(target_DVH.D95) + ' Gy')
print('D5 = ' + str(target_DVH.D5) + ' Gy')
print('D5 - D95 = {} Gy'.format(target_DVH.D5 - target_DVH.D95))
D95 = 10.938720703125 Gy
D5 = 16.332785866477273 Gy
D5 - D95 = 5.394065163352273 Gy
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 32.218 seconds)
